AI Architecture & Strategy
The Modern AI Stack: How Enterprises Integrate LLMs, Gateways, and Tools in 2025
AI has moved far beyond direct LLM API calls. Modern enterprise systems now rely on gateways, context services, orchestration layers, and tool interfaces that together form a reliable and governed AI platform. This article maps the functional pieces and the integration patterns that are emerging as the new baseline for AI-enabled organizations.

1. The Enterprise AI Stack Has Become Layered
Early adoption leaned on simple API calls. Today, teams need governance, consistency, and observability—leading to a three-layer architecture: application layer, orchestration layer, and model layer. Each solves a different set of problems.

1.1 The Application Layer
This is where users interact with AI: web apps, mobile apps, internal tools, and workflow triggers. The application layer defines user intent but rarely speaks directly to LLM providers anymore.
1.2 The Orchestration Layer
The orchestration layer includes gateways, retrieval systems, safety filters, and MCP servers. It acts as an AI control plane—packaging context, routing requests, and enforcing policy before any model sees a prompt.
1.3 The Model Layer
Enterprises now rely on multiple providers—OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Mistral, Meta, and inference hosts. Routing between models is becoming standard as organizations optimize for cost, speed, or task fit.
2. How These Layers Interact
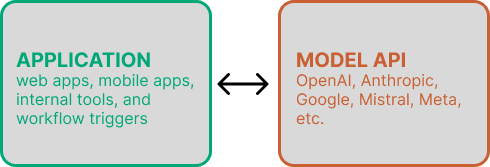
2.1 Pattern A — Direct API
Used mainly for prototypes. Lacks governance, routing, and operational reliability.
2.2 Pattern B — Gateway-Centered Applications
The dominant enterprise pattern: client → gateway → provider. Gateways enforce policy, redaction, observability, and model selection.
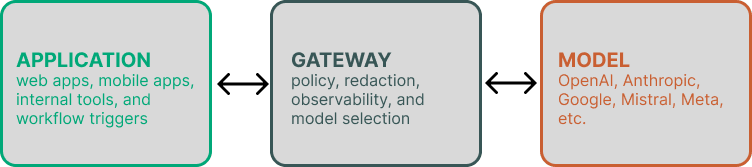
2.3 Pattern C — MCP-Driven Applications
MCP turns LLMs into structured agents. The LLM interacts with tools like file systems, data queries, calendars, or APIs in a controlled, permissioned environment.
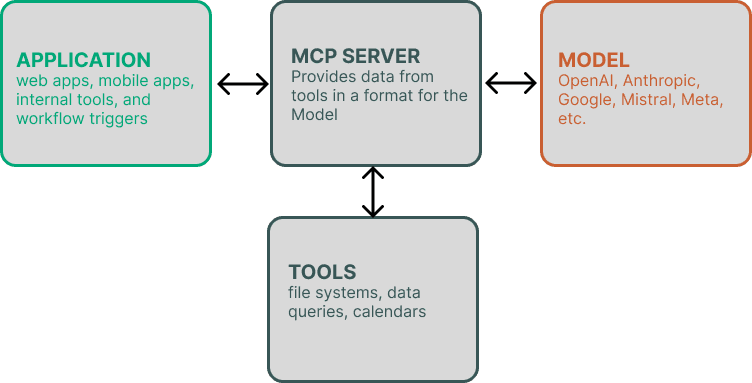
2.4 Pattern D — Hybrid Architecture
Larger organizations mix gateways, MCP, retrieval, and multi-model routing. This pattern is emerging as the backbone of modern AI platforms.
3. Real Examples of Enterprise AI Integration
3.1 Customer Support Copilot
A gateway handles redaction and policy controls. Retrieval enriches the prompt. The LLM generates responses that are stored and auditable.
3.2 Developer Assistant in the IDE
MCP provides access to code tools like file reading, refactoring, or test generation—within a tightly governed boundary.
3.3 AI Knowledge Search
RAG pipelines combine embeddings, search, and reranking to provide grounded answers and citations. Multi-model routing optimizes cost and performance.
3.4 Back-Office Automations
Events trigger the gateway, which calls LLMs for classification, summarization, or workflow QA. Responses are validated and routed into downstream systems.
4. Recommendations for Enterprise Teams
Start with a gateway for governance, add MCP for safe capabilities, use multi-model routing, incorporate human-in-the-loop flows, and document architecture early for audit and procurement stakeholders.
5. Closing Thoughts
The modern AI stack mirrors other enterprise systems—layered, governed, observable, and composed of interchangeable parts. Organizations that treat AI as an operational platform, rather than a single model, are shipping more reliable and scalable systems.
Need help designing safer digital experiences for young users?
We can assist with data audits, technical architecture, and safety‑by‑design reviews tailored to your goals and constraints.
Get notified when we publish
Join our newsletter for new articles on security, architecture, and delivery—no spam, unsubscribe anytime.